Touchless AC Current Detector
Welcome to Robotshapers .Non-contact AC current detection using transistors is a simple and effective way to detect the presence of AC current without direct electricity. This circuit, using the properties of transistors, can detect the magnetic field created by the changing current and output signal accordingly. Visit robotshapers.com for more information.
This circuit contains a transistor, some passive components and a coil. The coil acts as a sensor that collects the magnetic field produced by the alternating current. This changing magnetic field induces a small voltage across the coil which is amplified by the transistor.
When there is a change in current, the amplified signal causes the transistor to turn on and produce an output signal. This output can be used to trigger an alarm, activate a relay, or interact with other electronic devices to indicate the presence of AC current.
The non-contact nature of this circuit has many advantages such as security, convenience, and intrusion. It reduces the risk of electric shock by eliminating the need for direct contact with live wires. Also, it makes it easy and does not damage electronics.
Components required:
Circuit diagram:
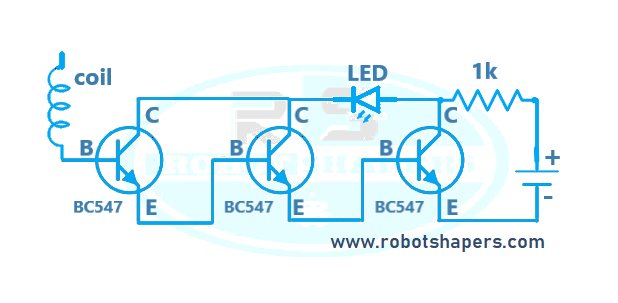
Working:
The non-contact AC current detector works on the principle of magnetic induction. It detects magnetic fields created by alternating current (AC) without direct electricity. It works like this:
- Induced Magnetic Field: Non-contact AC current detectors usually have a coil or loop sensor. When an alternating current flows through a nearby conductor, it creates a magnetic field around it. A loop sensor detects this magnetic field.
- Induced Voltage: According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, a changing magnetic field induces a small voltage in the sensor circuit. The magnitude of the induced voltage is proportional to the strength of the magnetic field, which is proportional to the current flowing through the conductor.
- Amplification: The induced voltage produced by the sensor loop is generally weak. To facilitate capture, the signal is amplified using electronic devices such as transistors or operational amplifiers (op-amps). The amplification stage raises the voltage to a level that the circuit can handle or use more of.
- Signal processing: After amplification, the signal can be processed according to the specific application. It can be used as an alarm, to open a relay, or to interact with other electronic devices.
Applications:
Non-contact AC current detectors have many practical applications in different industries. Here is an example of this application:
- The non-contact AC current detector is widely used in energy analysis and electrical energy monitoring.
- Using these probes, energy analysts and energy managers can measure the energy consumption of various electronic devices and machines without physically accessing or interfering with power.
- The probe can be used to measure current flowing through power lines, relays or individual devices.
- Wirelessly sensing and measuring AC current, these devices provide real-time information for accurate charging, balancing, and energy management.
- The uninterrupted nature of the non-contact AC current ensures minimal interruption to continuous operation, improves security during electrical inspections, and allows efficient electrical monitoring without the need for expensive equipment or complex installations.
Best projects development in Bhilai, Chhattisgarh, India. Contact : 7067150002

 robotshapers1
robotshapers1 


















